In June of 2015 we presented 5 Ways to Gain Back Floor Space. Today we highlight 4 more potential solutions to gain back valuable square footage in your warehouse.
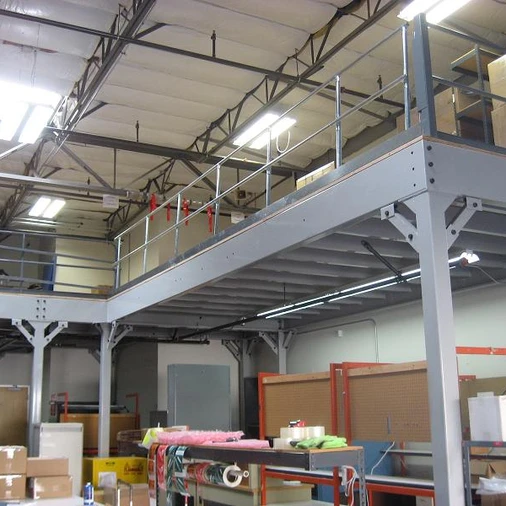
#1 Freestanding Mezzanine
Warehouses with clear heights exceeding 20′ can potentially add valuable square footage allowing unused space to be utilized within the vertical cube. Free standing mezzanines typically have a 125 lbs/ per square foot capacity allowing up to 2,000 lb pallet storage on the mezzanine level. Free standing mezzanines provide a significant increase of floor space. When compared to the costs of warehouse relocation or new construction, mezzanines can yield valuable savings There is also the alternative solution of a pallet rack supported mezzanine which can prevent requirements for footings and still provides for an increase to the warehouse footprint. Mezzanines can be removed and relocated to a future warehouse for increased value of ownership.
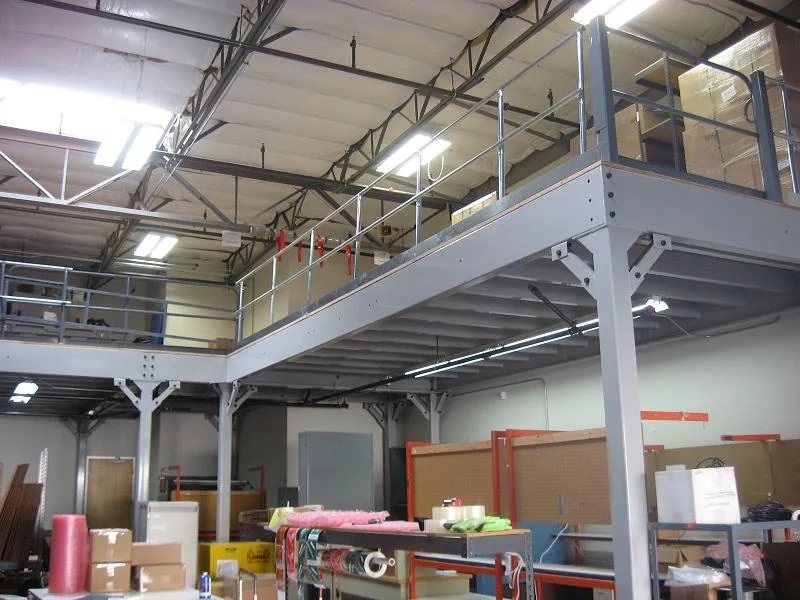

#2 Overdock Pallet Storage
The loading dock area typically goes under utilized as strictly a loading and unloading area. The real estate above the loading dock is a perfect location to store empty pallets.

#3 High Density Pallet Storage:
Double deep
A double deep rack system allows for storing pallets two deep. This system is used in conjunction with a double deep reach truck. Double deep is a higher density storage that has a much lower initial cost of ownership compared to alternative high density pallet storage systems. There is a 50% increase in storage capacity compared to selective rack. Some of the limitations of a double deep system are the fact that there is poor visibility of the rear pallet at higher beam elevations. Double deep is LIFO – Last in First out configuration.
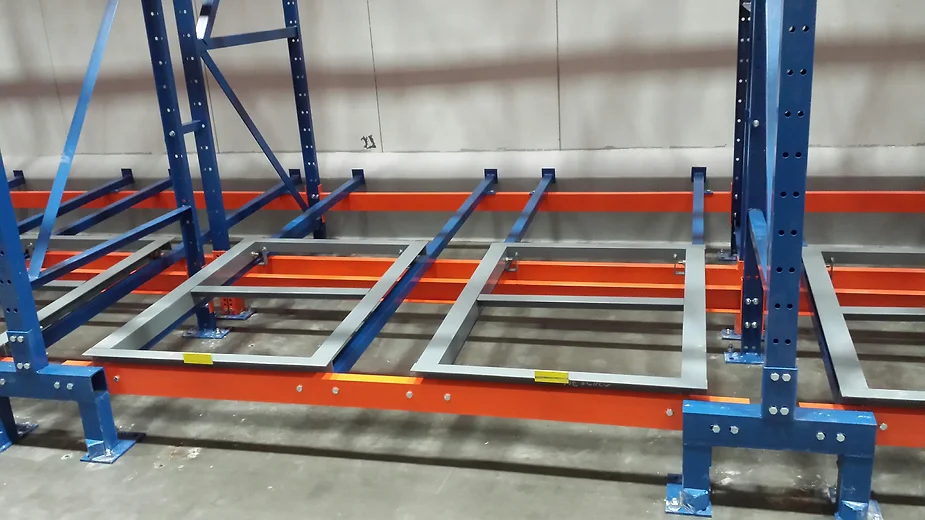
Push Back
Push back pallet rack systems are designed around the principle of organizing space by depth rather than width. This depth arrangement greatly reduces aisle space and increases storage density. In this configuration, each bay can be up to six pallets deep; each pallet stored on wheeled carts that fit onto rails. The rails are slightly angled toward the load/unload side of the rack in order to take advantage of gravity, saving enormous amounts of energy for moving heavy pallets. When a forklift sets the pallet onto the cart, it drives forward and causes the pallet to bump the next pallet, causing the entire row of pallets to roll backwards. When removing a pallet from the front position the remaining pallets immediately stage themselves forward so that the next available pallet can be accessed. Push back rack is a LIFO (last in, first out) storage system.

Pallet Flow
Pallet flow systems are high density pallet storage systems that utilize depth to increase capacity. This system uses a slightly inclined rail with rollers that allow pallets to move easily along the sloped plane. These systems are also called gravity flow or dynamic flow systems. The pallet flow system often has complex motion and braking systems to control the speed of the moving pallet. Pallet flow racking systems are either a FIFO (first in, first out) or a LIFO (last in, first out) storage system. If the system is loaded from the back and unloaded from the front, its FIFO; if the system is loaded and unloaded from the front its a LIFO system.

#4 Forklift Aisle Reduction VNA Forklift (Bendi/Drexel)
Majority of counterbalance sit down forklifts require a 12′ aisle to operate. Standup reach trucks can operate in as tight as a 9’6″ aisle. For an even greater reduction in aisle width, a very narrow aisle forklift is a potential solution. A Bendi forklift can operate in as small as a 6′ aisle, can lift up to 30′ tall and handle up to 3,000 lb loads.

